GUI编程
组件:
窗口、弹窗、面板、文本框、列表框、按钮、图片、监听事件、鼠标、键盘事件
1、简介
GUI的核心技术: swing 、AWT
-
现在很少使用的原因
- 界面不美观
- 需要jre环境
-
为什么还要学习?
- GUI是MVC框架的基础,可以了解MVC,了解监听
- 可以写一些自己想要的小工具
- 以后可能有极小的概率需要去维护swing界面
2、AWT
2.1、AWT介绍
- 包含很多类和接口,可以通过查看源码去了解
- 元素:窗口、按钮、文本框…
- java.awt
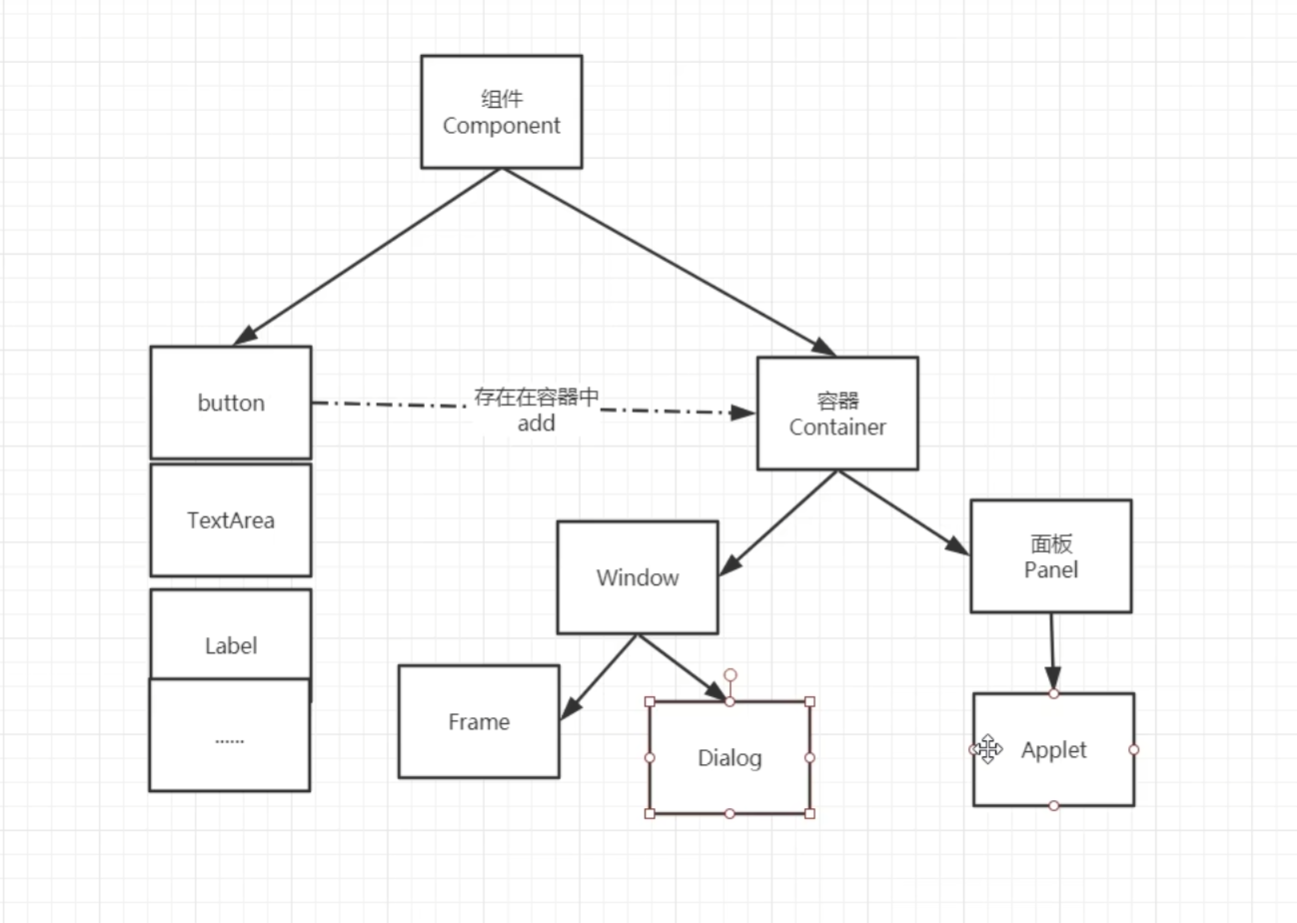
2.2、组件与容器
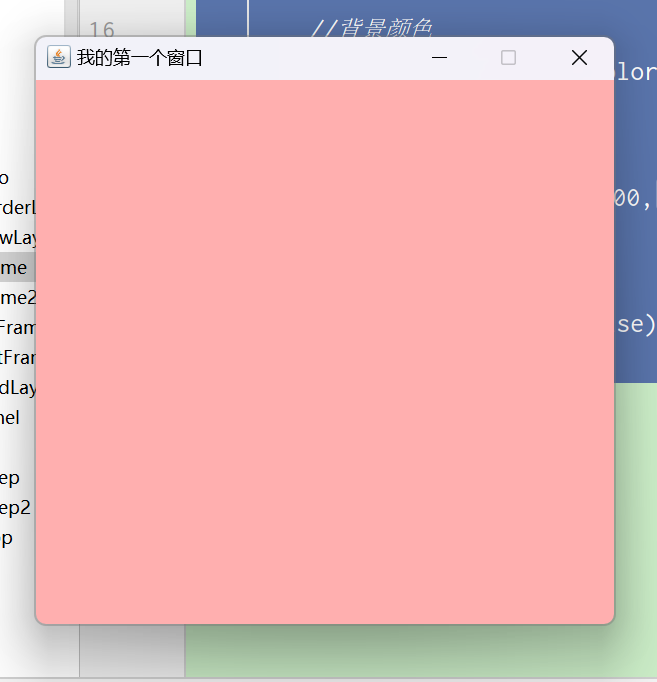
1、Frame
- 创建一个弹窗
1 | import java.awt.*; |
效果图:
- 创建多个弹窗
1 | import java.awt.*; |
效果图:
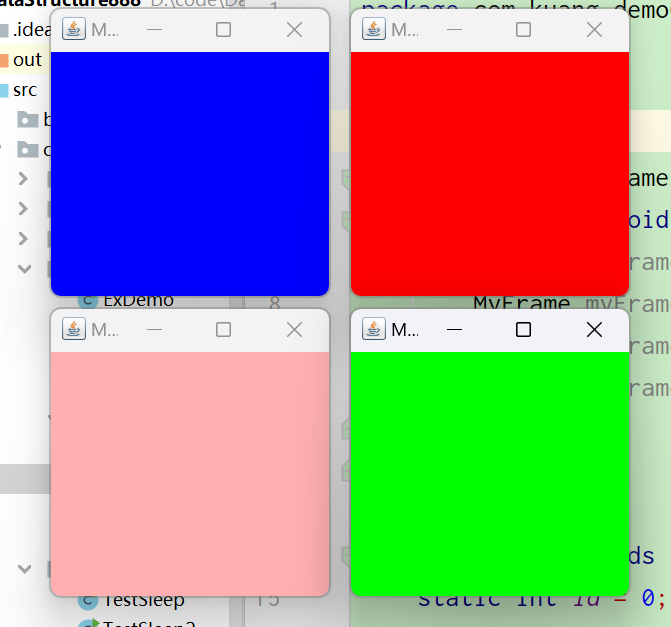
注:发现窗口关不掉,只有停止Java程序才能将其关闭
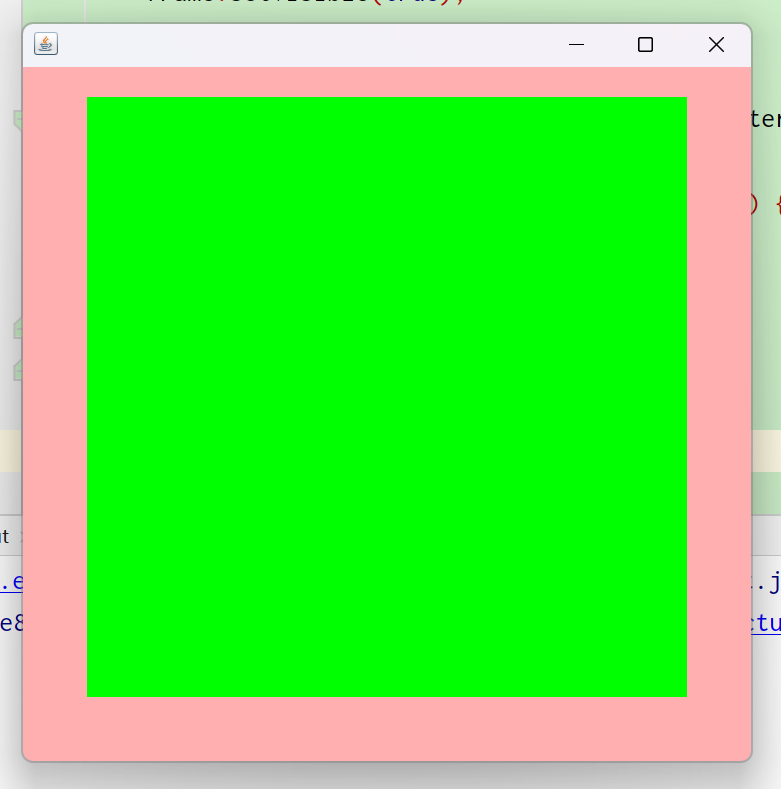
2、面板Panel
解决了关闭窗口的问题
1 | import java.awt.*; |
效果图:
3、布局管理器
流式布局
1 | import java.awt.*; |
效果图:
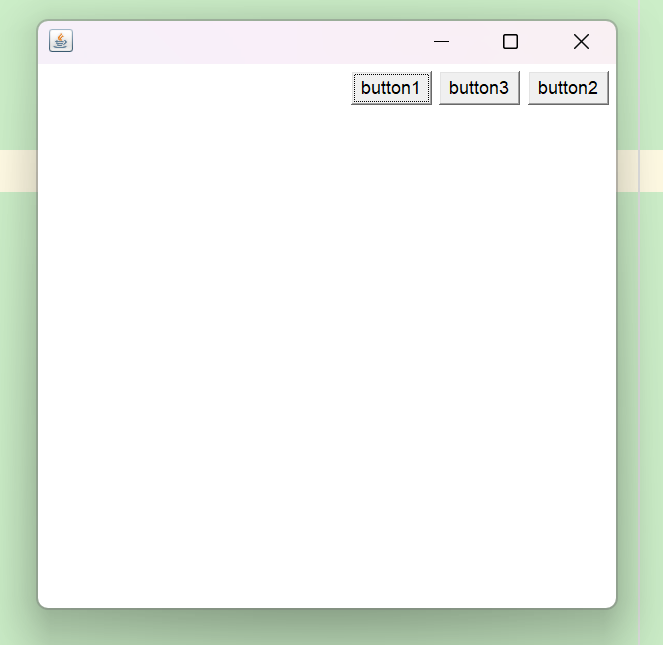
东南西北中
1 | import java.awt.*; |
效果图:
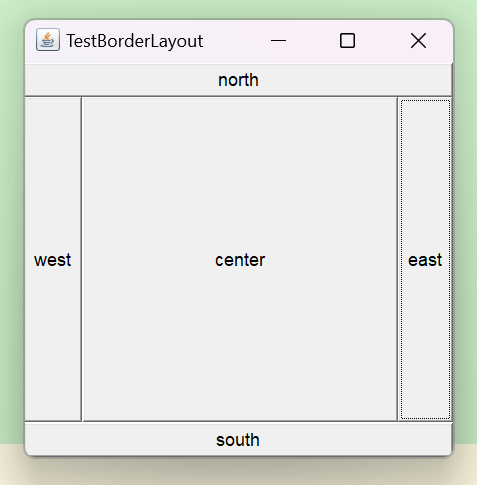
表格式布局
1 | import java.awt.*; |
效果图:
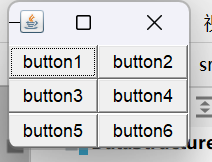
小题一道
通过对三种布局的使用,使其实现如下图效果:
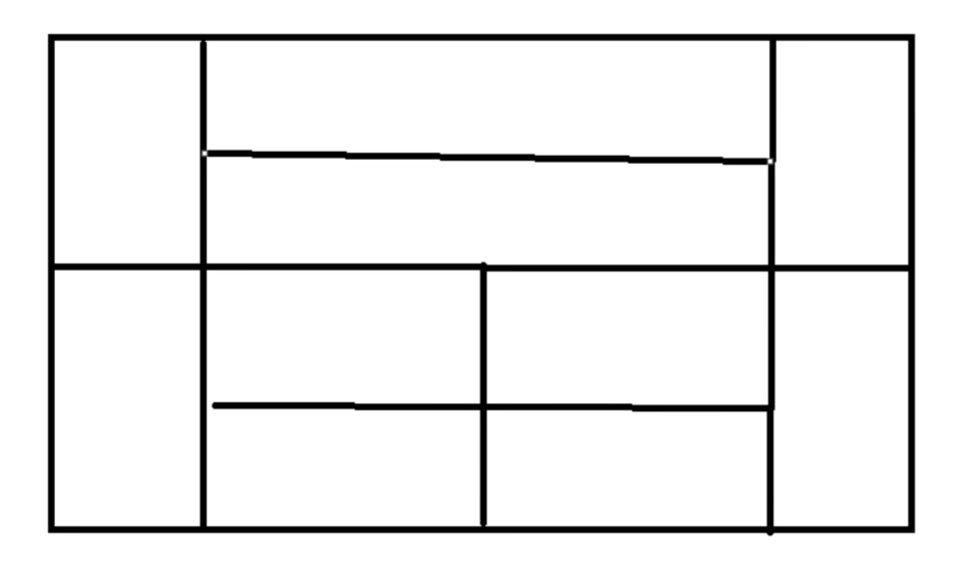
分析:
首先将该图分为上下两个面板
再将上面板分为左右两个按钮和中间一个面板,其中中间面板可以采用一列两行的表格式布局或者采用上下东南西北中布局中的西东
再将下面板分为左右两个按钮和中间面板,将中间面板采用表格式布局
- 参考答案
1 | import java.awt.*; |
效果图:

4、事件监听
事件监听:当某个事情发生的时候,干什么?
写一个事件监听-代码实现
1 | import java.awt.*; |
4.1、多个按钮,共享一个事件
1 | import java.awt.*; |

